SNMP Monitoring
What Is SNMP?
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for managing devices on IP networks, such as routers, switches, servers, and workstations. By utilizing an SNMP monitoring tool like Netdata, network administrators are able to collect and organize information about devices in real-time to ensure efficient functioning and to identify issues before they escalate.
Monitoring SNMP With Netdata
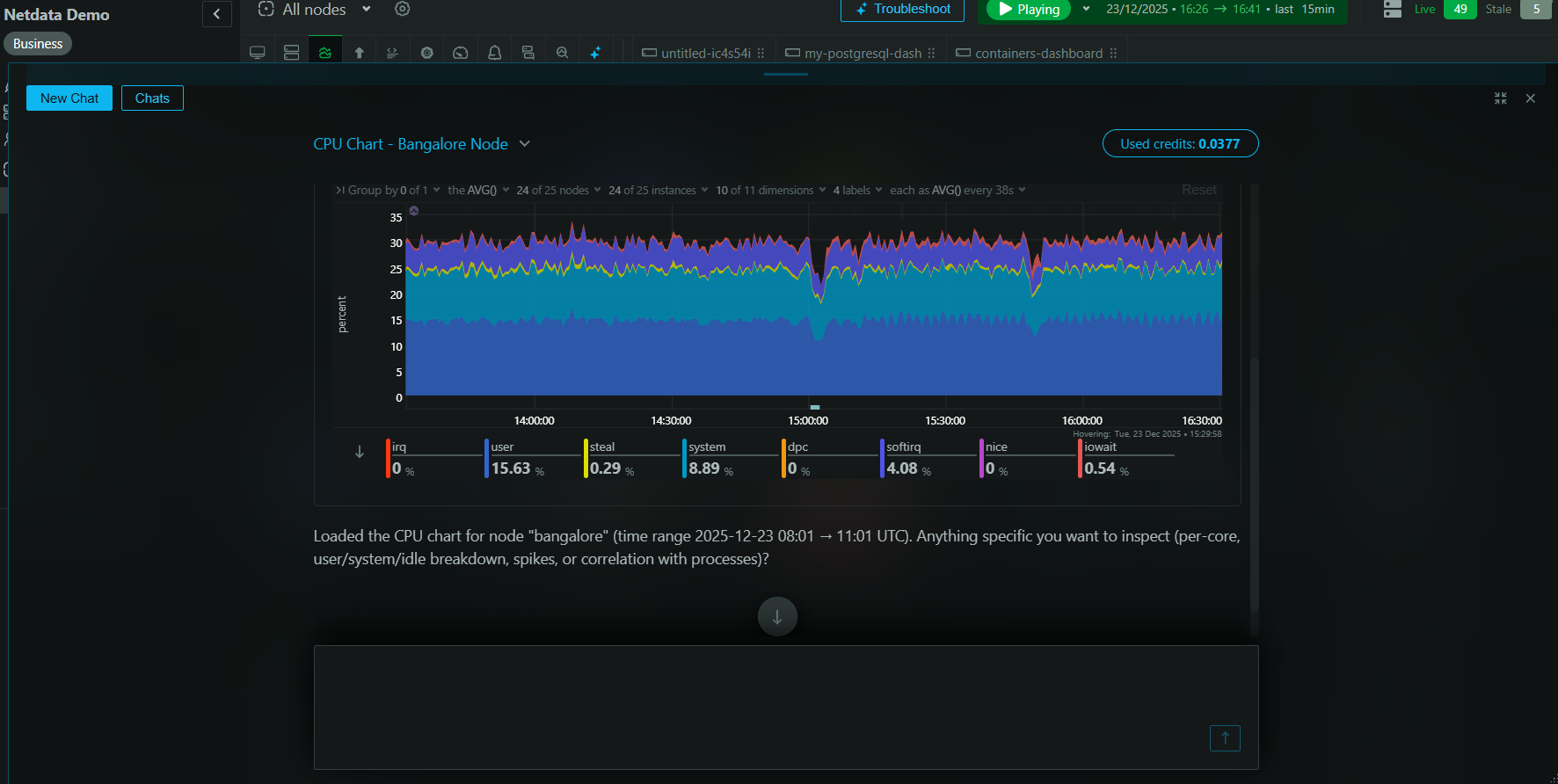
Netdata allows you to seamlessly monitor SNMP-enabled devices by leveraging its SNMP collector module. Whether you’re looking to track network interface traffic, errors, or overall uptime, Netdata provides tools for monitoring SNMP with minute precision. For those interested in configuring the monitoring setup for their SNMP devices, check out the SNMP Collector Documentation.
Why Is SNMP Monitoring Important?
An SNMP monitoring tool is crucial for ensuring the reliability and performance of network components. Monitoring SNMP facilitates the quick detection of anomalies such as traffic bottlenecks or errors, allowing network administrators to address potential issues swiftly before they affect users.
What Are The Benefits Of Using SNMP Monitoring Tools?
Using tools for monitoring SNMP devices ensures that network managers can:
- Identify and resolve problems before they impact customers.
- Optimize network performance by observing traffic patterns and bandwidth usage.
- Maintain compliance and security protocols through comprehensive network oversight.
Understanding SNMP Performance Metrics
To effectively use Netdata as an SNMP monitoring tool, it’s important to understand key performance metrics.
- Traffic: Measures the amount of data sent and received across network interfaces.
- Packets: Tracks unicast, multicast, and broadcast packets through each interface.
- Errors: Monitors errors in packet processing and transmission.
- Discards: Checks discarded packets that the interface was unable to process.
- Uptime: Keeps track of the total operational time of the SNMP device.
Key SNMP Metrics Table
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
snmp.device_uptime | Uptime of the SNMP device (in seconds). |
snmp.device_net_interface_traffic | Traffic through a device’s network interfaces, measured in kilobits per second. |
snmp.device_net_interface_unicast | The rate of unicast packets processed per second. |
snmp.device_net_interface_errors | The number of errors occurring during packet transmission. |
Advanced SNMP Performance Monitoring Techniques
For advanced users, Netdata allows the manual specification of custom OIDs to retrieve specific data points that go beyond default metrics. By doing so, users can create tailored monitoring experiences that drive deeper insights into SNMP device performance.
Diagnose Root Causes Or Performance Issues Using Key SNMP Statistics & Metrics
Netdata’s real-time monitoring capabilities enable users to quickly detect and diagnose problems within SNMP-managed environments. Whether it’s diagnosing root causes of errors or identifying performance bottlenecks, monitoring SNMP with Netdata ensures heightened network reliability.
Close out potential network issues by taking a look at Netdata Live and experience superior monitoring firsthand: Check out the Live Demo or Sign up for a Free Trial.
FAQs
What Is SNMP Monitoring?
SNMP monitoring involves collecting and analyzing data from SNMP-enabled devices in order to ensure their health and performance.
Why Is SNMP Monitoring Important?
Monitoring SNMP devices helps in maintaining the network’s stability by quickly identifying and addressing potential issues.
What Does An SNMP Monitor Do?
An SNMP monitor collects various performance metrics from network devices, providing insights that help optimize device performance and network health.
How Can I Monitor SNMP In Real-Time?
Real-time monitoring of SNMP devices is made possible with Netdata’s dashboard, offering seamless data visualization and immediate notifications for performance anomalies.